迭代模式
代器模式就是顺序访问聚集中的对象,一般来说集合类中非常常见。这句话包含两层意思:一是需要遍历的对象,即聚集对象Collection,二是迭代器对象Iterator,用于对聚集对象进行遍历访问
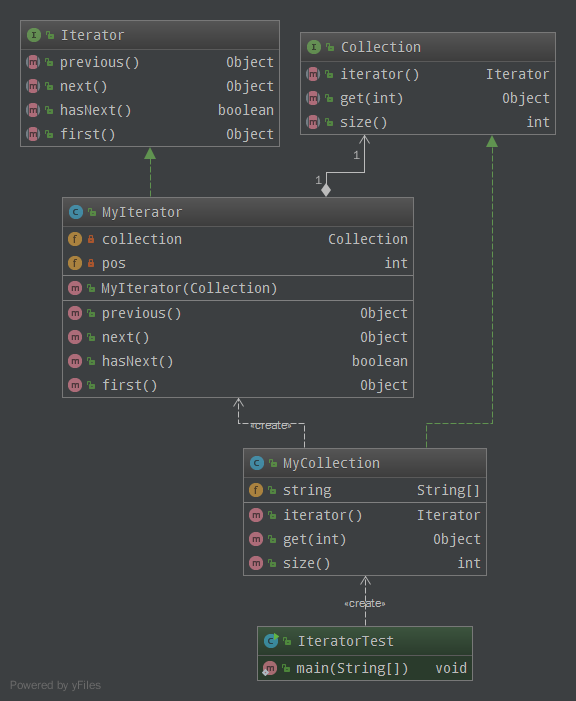
UML
Java
- 定义迭代操作接口Iterator:
public interface Collection { Iterator iterator(); /*取得集合元素*/ Object get(int i); /*取得集合大小*/ int size(); }
- 定义集合接口Collection,注意:集合接口可以返回迭代接口:
public interface Collection { Iterator iterator(); /*取得集合元素*/ Object get(int i); /*取得集合大小*/ int size(); }
- 实现迭代接口:
public class MyIterator implements Iterator { private Collection collection; private int pos = -1; public MyIterator(Collection collection) { this.collection = collection; } @Override public Object previous() { if (pos > 0) { pos--; } return collection.get(pos); } @Override public Object next() { if (pos < collection.size() - 1) { pos++; } return collection.get(pos); } @Override public boolean hasNext() { if (pos < collection.size() - 1) { return true; } else { return false; } } @Override public Object first() { pos = 0; return collection.get(pos); } }
- 实现具体的集合对象:
public class MyCollection implements Collection { public String string[] = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"}; @Override public Iterator iterator() { return new MyIterator(this); } @Override public Object get(int i) { return string[i]; } @Override public int size() { return string.length; } }
- 测试类:
public class IteratorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection collection = new MyCollection(); Iterator it = collection.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
- 测试结果:
A B C D E
注意,这个实现至少有以下几个缺点:
- 线程不安全
- 类型不安全
- 缺少比较器
Scheme
- 语言原生的map/reduce函数:
(map (lambda (s) (begin (display s) (newline) s)) '(a b c d e)) ;; => a ;; b ;; c ;; d ;; e ;;Value 16: (a b c d e)